Wapiti is an open source tool that scans web applications for multiple vulnerabilities including data base injections, file disclosures, cross site scripting, command execution attacks, XXE injection, and CRLF injection. The database injection includes SQL, XPath, PHP, ASP, and JSP injections. Command execution attacks include eval(), system(), and passtru() vulnerabilities.
Besides identifying the aforesaid vulnerabilities, Wapiti also performs some addition penetration testing tasks, such as finding potentially dangerous files on servers, finding configuration errors in .httaccess files that can lead to security breach, and finding backup copies of the applications on the server that could compromise the security of said web applications if an attacker manages to get a hand on those files. The results gathered are automatically stored in a html file. The other supported file formats include .XML, .JSON, and .TXT.
Wapiti Installation
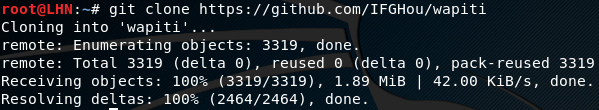
Wapiti requires Python 2.7.x or higher to operate. The other dependencies include Python-requests, and Python-xml. To begin with installation, first clone the tool from Github using the following command.
https://github.com/IFGHou/wapiti
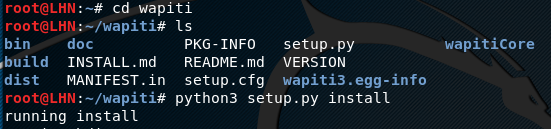
In the next step, run the setup.py file from wapiti directory using the following command.
cd wapiti python3 setup.py install
How Wapiti Works
To scan your test web application for possible vulnerabilities, run the following command.
Python3 wapiti –u <web application>
Wapiti has dedicated modules for each type of vulnerability it scans. Before scanning the target for any vulnerability, Wapiti enumerates the links associated with the target web application. Once links are enumerated, Wapiti runs each module one by one to test if the target web application is vulnerable. The details found about vulnerabilities are stored in a file, generated at the end of scanning. Wapiti has the capability to resume any scan process if aborted in the middle.
The other features of the tool include support for HTTP and HTTPS proxy, excluding unwanted urls from the scanning process, extracting the urls from JavaScript and Shockwave Flash files, and support for authentication.
If we run Wapiti on the following test website, it scans and displays the vulnerabilities instantly.
python3 wapiti –u http://phptest.vulnweb.com
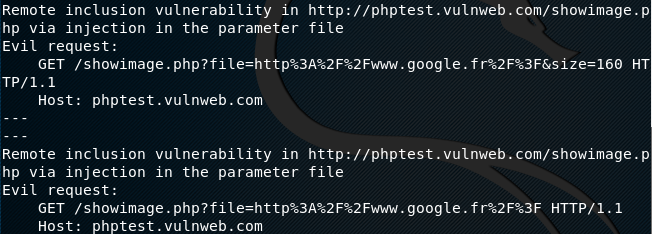
The complete vulnerability report is generated and stored in the root folder as shown in the following screenshot.
The generated html report can be analyzed in a web browser. The report shows all the results in a tabular format as shown in the following format.

The details of vulnerabilities can be found by clicking on the listed vulnerability.
What Bunny rating does it get?
Wapiti is pretty handy in scanning web applications against critical vulnerabilities. The tool supports payload options with both, GET and POST method of attacking the target application. Although the overall performance of Wapiti is decent, the tool sometimes hangs while scanning large web applications. As a result we will be awarding this tool a rating of 3.5 out of 5 bunnies.



![]()
Want to learn more about ethical hacking?
Do you know of another GitHub related hacking tool?
Get in touch with us via the contact form if you would like us to look at any other GitHub ethical hacking tools.