It hasn’t been long since we studied how Android apps evade app permissions to exfiltrate user data. Once again, researchers have conducted another study to reveal how Android apps listen to users’ conversation over loudspeakers. Dubbed ‘Spearphone’ the attack empowers perpetrators to capture all voice generated through a device’s loudspeaker.
Spearphone Attack Breaching Speech Privacy
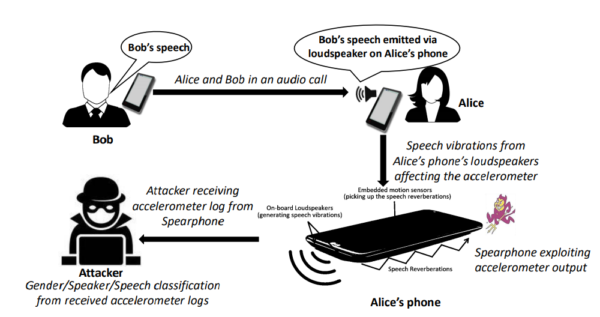
Researchers have demonstrated a new side-channel attack ‘Spearphone’ that allows capturing loudspeaker data. The Spearphone attack breaches speech privacy by exploiting the motion sensor ‘accelerometer’ and capturing speech reverberations generated through the loudspeaker. This, in turn, empowers the attackers to listen to every sound coming out of the loudspeaker including conversations, music, or any other audio.
As elaborated in their research paper, this vulnerability exists in most Android smartphones currently in use. The users become vulnerable to attacks as soon as they put their phones to loudspeaker mode when playing any audio files, during phone calls, or interacting with voice assistants.
Describing the Spearphone attack, the researchers stated,
Spearphone is a three-pronged attack that performs gender, speaker and speech classification using accelerometer’s response to the speech reverberations, generated by the victim’s phone’s speakers.
According to this study, the flaw exists owing to the placement of accelerometer and loudspeaker on the same surface within a smartphone.
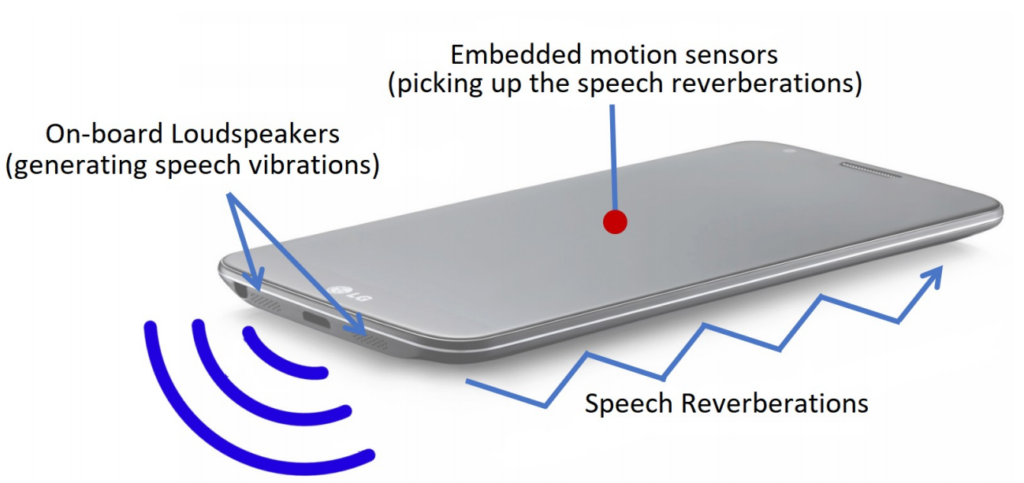
Since the accelerometer can sense the sound reverberations at certain loudness, it can capture the voice generated from the loudspeaker. Thus, an attacker can exploit this glitch via a malicious application that can abuse accelerometer to capture loudspeaker sounds.
Demonstration of Attack on Android Phones
As a PoC, the researchers designed an Android app with malicious intent to capture accelerometer readings. They also elaborate that the same attack can also make use of a malicious Javascript running on the target phone’s browser.
For test devices, they took LG G3, Samsung Galaxy S6 and Samsung Note 4. Whereas, they conducted the experiment into two different setups for precise results – handheld setup and surface setup (device placed on a hardwood top).
Here is how the researchers have illustrated the attack scenario in case of a phone call.
And, in case of media playback or interaction with voice assistants.
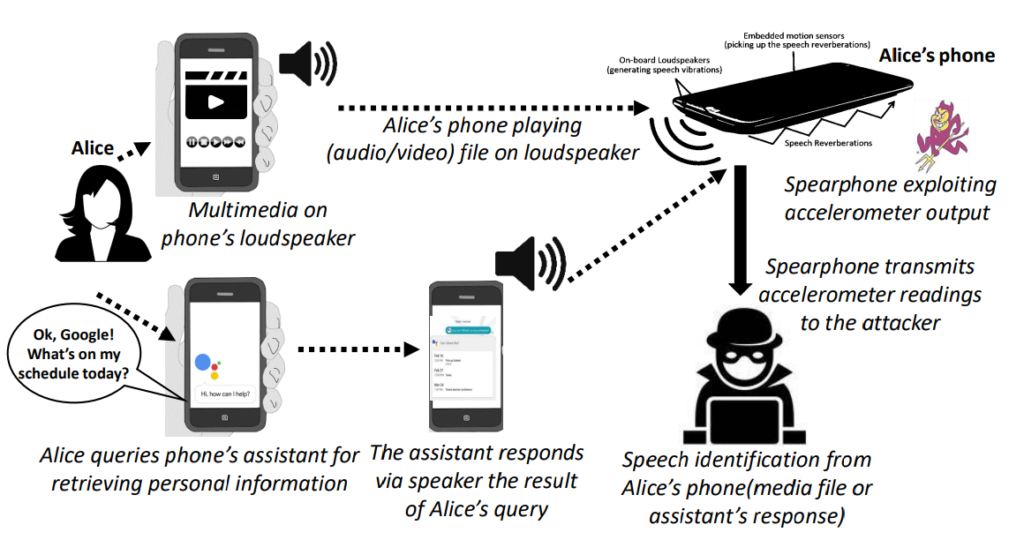
The researchers primarily conducted this study on Android phones owing to their dominant market share and the ease of access by applications to a motion sensor. However the motion sensor ‘accelerometer’ was found to be more receptive to Spearphone attack than ‘gyroscope’.
Though, their study had some limitations that they have stated in their paper. This does not alleviate the dangers associated with this attack.
The researchers have advised implementing strict usage permission policy for Android apps as a possible mitigation. Moreover, users should also remain careful when allowing apps to access motion sensors on their devices. Besides, using vibration dampening material around the built-in loudspeakers on the device may also help mitigate the attack.
This isn’t the first time that a study has demonstrated the vulnerability of motion sensors. Earlier, researchers have demonstrated a sensor calibration attack involving motion sensors to track users’ online activities.
Let us know your thoughts in the comments.

