Researchers have found a new malware, “Ducktail,” that attempts to hack Facebook Business accounts via LinkedIn. Specifically, the malware reaches the target victims via phishing attacks through LinkedIn, ultimately infecting the device to scan for Facebook account details.
Ducktail Malware Hacks Facebook Business Accounts
In a report elaborating on the details of the Ducktail malware campaign against Facebook Business accounts, the WithSecure Intelligence Research team shared how they noticed the phishing campaign exploiting the LinkedIn platform.
Specifically, the threat actors behind this campaign typically target Facebook accounts using Facebook Ads and Business services. After identifying those accounts, the attackers reach out to their LinkedIn profiles (which business users generally maintain), delivering them the malware. The researchers believe the attackers might have adopted this uncanny strategy to stay under the radar.
Upon reaching the target device, the Ducktail malware stats executing its malicious activities. It exhibits different features, including stealing stored information from disks, scanning browsers to steal data (particularly for Facebook account-related details), and stealing other data.
After exfiltrating the data, the malware sends it to its Telegram C&C servers.
The following image shows the attack method of the Ducktail malware. The researchers have shared the technical details about the attack in their report.
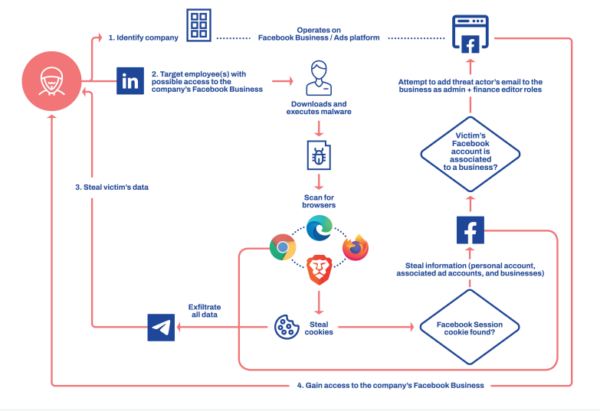
Source: WithSecure
According to WithSecure, tracing back the campaign reveals the attackers’ location in Vietnam. The malware has been running active campaigns since July 2021. But the researchers have observed the malware active in the wild since 2018.
This malware campaign is an interesting case of targeting one social media platform via the other. It demonstrates how users should avoid linking their profiles across different platforms or cross-sharing the details.
Similarly, since staying private isn’t practical for business accounts, they must remain cautious when interacting with strangers. Accepting messages from suspicious profiles, connecting with random accounts, and trusting every incoming message to share personal details or click links, are some practices that users must avoid.

