Security Researchers at Palo Alto Networks discovered that a hacker has used a poor choice of encryption to encrypt their malware. The new malware discovered was used in various targeted attacks and coined the name “Chainshot”.
Researchers discovered the malware in parts of an Adobe Flash Zero-day exploit (CVE-2018-5002) the code had also been used in a series of the malware campaigns.
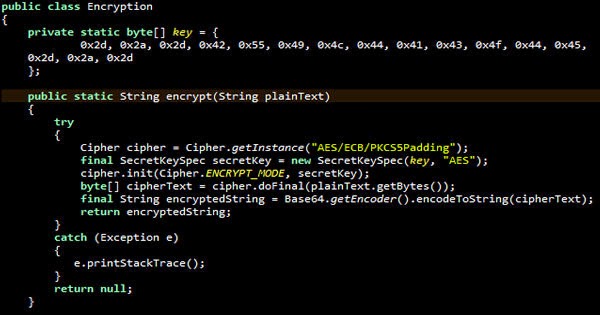
When the security researchers studied network captures of the traffic exchanged with the attacker’s command and control servers they observed that the malware has been using a 512-RSA key. The RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) uses an asymmetric key algorithm.
How does the RSA Asymmetric Algorithm Works?
The Asymmetric key algorithm uses a public/private key pair to encrypt and decrypt data. Cracking a 512-bit key has been potentially possibly since 1999, however the computing power required would be immense. Nowadays all you need is money and you can rent such computing power from the cloud. The technical report published by the researchers explains how the private key was decrypted.
“While the private key remains only in memory, the public keys’ modulus n is sent to the attacker’s server. On the server side, the modulus is used together with the hardcoded exponent e 0x10001 to encrypt the 128-bit AES key which was used previously to encrypt the exploit and shellcode payload,” they write.
How did the Researchers crack the Encryption?
Using Factoring as a Service (FaaS), the researchers were able to calculate the decryption key and access the Chainshot malware.
Chainshot was also designed to bypass the Kaspersky and Bitdefender anti-virus solutions for both x86 and x64 based computers. Bitdefender have said that their users have been protected since July, Artem Baranov of Kaspersky said that he would test the exploit with their Automatic Exploit Prevention Component.
The main task of the Chainshot malware is to push additional malware on to the compromised machine, the last piece of malware that is dropped is designed to fingerprint the system which sends details of the processes running on the machine.
Take your time to comment on this article.